|
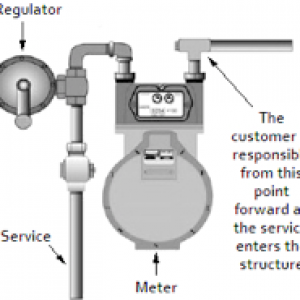
Maintaining Your Natural Gas Pipes Illinois Gas Company regularly monitors the pipelines up to your meter that deliver natural gas to your home or business for corrosion and leaks. You are responsible for maintaining the lines that begin at the meter and extend to the natural gas-burning equipment in your home or business, yard and any other buildings on your property. If there is more than three feet between your meter and your home, Illinois Gas Company will monitor the primary pipeline. However, you are still responsible for repairs. (Illinois Gas Company does not monitor any fuel lines after the meter for business or residential customers.) You should periodically have your buried gas piping inspected for corrosion and leaks and have repairs made if any unsafe condition is found. Also, any repairs, locating and appliance connector replacements and inspections should only be performed by a plumbing contractor, heating contractor or other qualified professional. When excavating near buried gas piping, the piping should be located in advance, and the excavation done by hand.
Appliance Connectors According to the Consumer Product Safety Commission, certain older gas connectors may be dangerous. Gas connectors are corrugated metal tubes used to connect gas appliances to fuel gas supply pipes. These older brass connectors have a serious flaw in how their tubing was joined to their end pieces.
Over time, the end pieces can separate from the tubing and cause a serious natural gas leak, explosion or fire. While these dangerous uncoated brass connectors have not been made for more than 20 years, many of them are still in use. And the possibility of failure still exists. The older these connectors get, the greater the possibility of failure. Uncoated brass connectors should be replaced immediately. Although not all uncoated connectors have this flaw, it is very difficult to tell which ones do. Therefore, any uncoated brass connector should be replaced immediately with a new plastic-coated brass connector or a new stainless steel connector.
Connectors can wear out from too much moving, bending, or corrosion. Moving the appliance, even slightly, whether to clean behind it or to inspect its gas connector, can cause the complete failure of one of these older weakened connectors and possibly result in a deadly fire or explosion. As a rule, you should replace the connectors whenever the appliance is replaced or moved from its location. Only a qualified professional should check or replace connectors. Do not move your appliance to check the connector! They can easily break if moved even slightly. For your safety, make sure a qualified professional performs the inspection and immediately replaces any uncoated brass connectors with stainless steel or plastic-coated connectors.
FLOOD SAFETYRespond Safely In Flood EmergenciesHeavy rains can cause flooding any time of the year. A few simple steps can keep your family safe if your basement floods:
Pipeline Safety Illinois Gas Company carefully maintains a network of natural gas mains and service pipelines that deliver natural gas to communities in SE Illinois. This comprehensive infrastructure provides the natural gas necessary to successfully serve our customers. Our priority is the safety of our customers and our employees. We are committed to maintaining a safe and reliable natural gas pipeline infrastructure that serves the needs of customers, including working with local/regional response officials located near our pipeline facilities to ensure a better understanding of the nature of our infrastructure and our emergency preparedness. About our natural gas pipeline safety management structure and regulation Illinois Gas Company Assistant General, & Safety and Compliance Manager, under the direction of the Chief Operating Officer and Professional Engineer, oversees the policies, standard practices and programs in regards to natural gas pipeline safety. This group of individuals acts as a liaison between Illinois Gas Company and state and federal regulatory agencies to ensure that the company complies with the various pipeline safety laws and regulations. For more information about pipeline safety, we encourage you to visit the following websites: Illinois Gas Company adheres to the Code of Federal Regulations Title 49: Part 191 & 192, issued by the Department of Transportation’s (DOT) Pipeline and Hazardous Material Safety Administration (PHMSA). Acting through the Office of Pipeline Safety, PHMSA administers the DOT’s national regulatory program to assure the safe transportation of natural gas, petroleum and other hazardous materials by pipeline. PHMSA requires that distribution systems comply with requirements for design, construction, testing, inspection, operations and maintenance from the point of connection to the Company’s system through transmission up to and including the gas meter that is connected to a home. Illinois Gas Company also complies with the requirements of Illinois Administrative Code Title 83. The Illinois Commerce Commission (ICC) enforces the Illinois Administrative Code Title 83: Public Utilities. The ICC’s Natural Gas Pipeline Safety division inspects natural gas pipeline facilities to ensure compliance with all Federal and State safety rules and regulations pertaining to the design, construction, operation and maintenance of those facilities. Natural gas lines are underground…but where?Natural gas companies, including Illinois Gas Company, install aboveground pipeline markers to indicate the approximate location of buried large diameter, high pressure gas transmission lines. These line markers display the name of the pipeline operator and the telephone number where the operator can be reached in case of an emergency. Line markers are placed at public road crossings except in urban areas. Pipeline markers and warning signs indicate only the presence of a pipeline. They should not be used or relied upon to determine the exact location of the pipeline. Pipeline Integrity To ensure safety, Illinois Gas Company works diligently to comply with the Gas Integrity Management Rule, established by the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration. This mandate requires Illinois Gas Company to identify high density population areas and perform periodic inspections of pipelines located in those areas. Our Pipeline Integrity Program describes these high density population areas, characterizes threats to the pipelines in these areas, describes how these pipelines will be tested, and how any defects will be evaluated and repaired. The effectiveness of this Program is monitored, and the Program is modified as needed to improve its effectiveness. Physical damage to the pipeline and facilities is considered one of the most severe threats to people and the environment. Our recently established Pipeline Integrity and Public Awareness Program ensures better protection from pipeline incidents. To learn more about pipeline integrity management, log on to the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration website www.npms.phmsa.dot.gov. Identifying Pipeline Damage Natural gas is colorless and odorless. That’s why utilities add an odorant called mercaptan to natural gas. Its unpleasant smell helps alert you in the event of a gas leak. The unintentional release of gas is dangerous to the public and could cause fires, explosions, injury, and even death. A gas leak or damaged pipeline is indicated by the following:
If you observe the above conditions, call the 800-633-6250 or 618-395-8588 emergency phone number, the number on the pipeline marker or 9-1-1 from another location.
|